Understanding the Brain, Nervous System, and Common Disorders
Introduction to the Brain and Nervous System
The brain is a complex and remarkable organ consisting of billions of nerve cells responsible for controlling various bodily functions, thoughts, emotions, behaviors, and sensory perceptions. It plays a pivotal role in processing information and maintaining consciousness. The nervous system, consisting of the brain and peripheral nerves, facilitates communication between different parts of the body.
Parts of the Brain
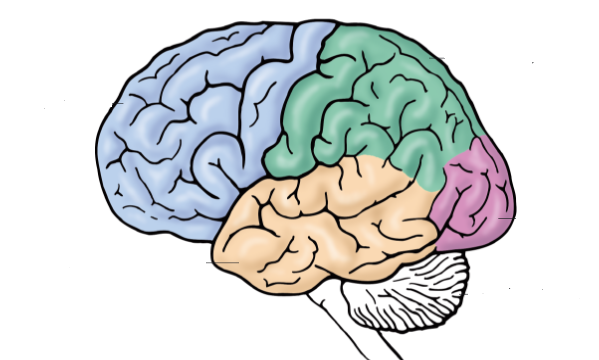
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum, is divided into two hemispheres responsible for different functions. It includes four lobes: frontal (thinking and movement), parietal (sensory interpretation), temporal (smell, sound, memory), and occipital (visual processing).
- Cerebellum: Located at the back of the head, the cerebellum regulates both conscious and unconscious movements and coordinates them based on sensory input.
- Brainstem: This vital part of the brain connects it to the spinal cord and controls essential functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration. It also influences sleep patterns.
The Nervous System
The nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (all nerves except those in the brain and spinal cord). The peripheral nervous system can be divided into the somatic nervous system (voluntary muscle control and sensory perception) and the autonomic nervous system (involuntary functions like heartbeat and digestion). The autonomic nervous system further splits into the sympathetic (fight-flight response) and parasympathetic (rest and recovery) divisions.
Common Brain and Nervous System Disorders
- ADD (Attention Deficit Disorder) and ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder): Neurodevelopmental disorders characterized by difficulties in attention, focus, and impulsivity.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: A progressive neurodegenerative disorder causing memory loss, cognitive decline, and changes in behavior.
- Dementia: A broader term for various disorders causing cognitive impairment and memory loss, including Alzheimer’s disease.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: A rare autoimmune disorder leading to muscle weakness, tingling, and paralysis due to damage to the peripheral nervous system.
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, often caused by infections.
- Brain Tumor: Abnormal growths of cells in the brain, which can be benign or malignant, and may cause various neurological symptoms.
- Huntington’s Disease: A genetic disorder leading to motor dysfunction, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): An autoimmune disorder that damages the protective covering of nerve fibers, causing a range of symptoms.
- Narcolepsy: A chronic sleep disorder characterized by sudden and uncontrollable episodes of sleepiness.
- Parkinson’s Disease: A progressive neurological disorder causing tremors, stiffness, and movement difficulties.
- Stroke: A sudden interruption of blood flow to the brain, leading to brain damage and various impairments.
These are just a few examples of brain and nervous system disorders. Each disorder presents with distinct symptoms and requires specific treatments, often involving a combination of medical interventions, therapies, and lifestyle adjustments.
Understanding the brain, nervous system, and common disorders is crucial for recognizing symptoms, seeking appropriate care, and managing these conditions effectively.