Getting to Know Kidney and Urinary Tract Health
Problems related to the kidneys and urinary tract can give rise to a range of uncomfortable symptoms, such as pain, burning sensations, difficulty in urination, or even involuntary leakage. These issues are quite common and can span various life stages, from childhood bedwetting to adult urinary tract infections and incontinence. In this comprehensive guide, we’ve compiled vital information about different diseases and conditions that impact the kidneys and urinary tract. Whenever you face concerns, remember that you can rely on our assistance to assess your problems effectively.
Understanding Kidney Function
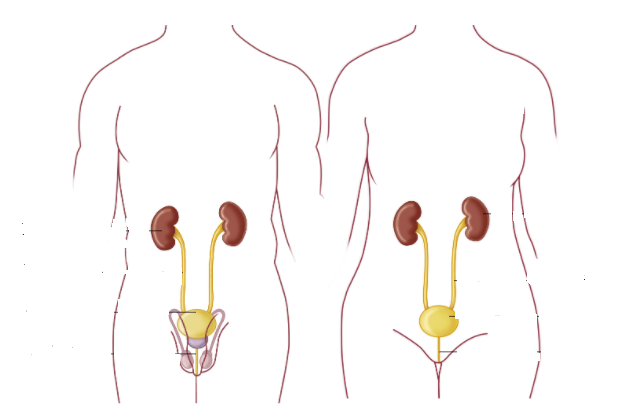
The kidneys, shaped like two beans and approximately the size of a clenched fist, measuring 10 to 12 centimeters in length, reside on either side of the spine. Connected to the bladder through tubes known as ureters, the kidneys play a pivotal role in producing urine, which is then transported to the bladder. Beyond this fundamental function, the kidneys serve several vital roles, including:
- Excretion of Waste Products: The kidneys facilitate the removal of waste products from the body through urine.
- Fluid and Salt Balance: These organs regulate the body’s fluid and salt balance to ensure optimal hydration and electrolyte levels.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Kidneys contribute to the regulation of blood pressure, helping to maintain cardiovascular health.
- Hormone Production: They are responsible for producing essential hormones that play a role in red blood cell production and bone health.
The Mechanics of the Urinary Tract
Urine formation begins within the kidneys and travels to the bladder through the ureters, narrow tubes connecting the two. Accumulating in the bladder, urine stretches its walls, which in turn triggers the sensation of needing to urinate. The bladder can accommodate approximately three to four deciliters of urine. When you decide to release the urine, it is emptied through the urethra, the final segment of the urinary tract. This tube is surrounded by a muscle under conscious control, allowing you to initiate urination.
Common Diseases and Conditions
Numerous conditions can affect the health of the kidneys and urinary tract. Some of the notable ones include:
- Blood in the Urine: Known as hematuria, this condition can arise from various factors and should be evaluated by a medical professional.
- Bladder Issues: Disorders affecting the bladder’s function can lead to urinary urgency, frequency, and discomfort.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: This condition involves inflammation of the female reproductive organs and may lead to complications within the urinary tract.
- Kidney Stones: Hard deposits formed within the kidneys can cause severe pain and affect urinary flow.
- Sork Fever: An acute bacterial infection, often seen in children, can result in kidney damage if not promptly treated.
- Bed Wetting: Common in childhood, this condition involves involuntary urination during sleep.
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): Bacterial infection affecting the urinary tract, causing symptoms like pain, burning, and frequent urination.
- Urinary Incontinence: This refers to involuntary leakage of urine, which can occur due to various factors and affect individuals of different ages.
- Overactive Bladder: Characterized by sudden and frequent urges to urinate, this condition can impact daily life and quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of kidney function and the urinary tract is essential for recognizing potential issues and seeking timely medical assistance. Whether it’s managing urinary incontinence or addressing kidney-related concerns, remember that knowledge is power, and by staying informed, you can take proactive steps toward maintaining optimal kidney and urinary tract health. If you’re ever uncertain about your symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out for professional guidance.