Getting to Know: Navigating Gastrointestinal Health and Disorders
Introduction: The proper functioning of the stomach and intestines is integral to overall health. This comprehensive guide delves into various disorders that affect the gastrointestinal system, ranging from common stomach issues to chronic conditions that impact daily life. The gastrointestinal tract, encompassing organs and processes from the mouth to the rectum, plays a pivotal role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall well-being.
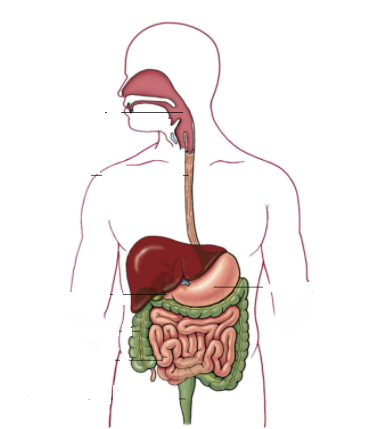
The Significance of the Gastrointestinal Tract: The gastrointestinal tract comprises a network of interconnected organs including the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum. Alongside these structures, glands and organs collaborate to ensure efficient digestion. Food travels from the mouth through the esophagus to the stomach, where gastric juices aid in breakdown and destruction of bacteria. Subsequently, the transformed food reaches the small intestine, where further digestion and nutrient absorption occur.
The Role of Intestinal Organs: The duodenum, situated at the beginning of the small intestine, plays a crucial role in digestion. Here, bile from the gallbladder and pancreatic enzymes collaborate to facilitate the breakdown of fats and other nutrients. The intestines also house the enteric nervous system, often referred to as the “abdominal brain,” containing over 100 million nerve cells that communicate with the central nervous system. The intestines are home to the intricate community of microorganisms known as the intestinal flora, which have been linked to various health conditions.
Gastrointestinal Disorders and Ailments: A spectrum of disorders can affect the stomach and intestines, leading to discomfort and disruptions in daily life. Some of these conditions include:
- Diarrhea: Experiencing frequent loose stools.
- Constipation: Difficulty passing stools, often accompanied by discomfort.
- Gases in the Stomach: Accumulation of gas leading to bloating and discomfort.
- Gluten Intolerance: Adverse reactions to gluten-containing foods.
- Heartburn: Burning sensation in the chest due to acid reflux.
- Hemorrhoids: Swollen blood vessels in the rectum causing pain and discomfort.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Chronic condition characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits.
- Colic: Severe abdominal pain caused by muscle contractions.
- Lactose Intolerance: Inability to digest lactose, leading to digestive discomfort.
- Gastric Catarrh: Inflammation of the stomach lining causing discomfort and nausea.
- Gastric Ulcer: Open sore on the stomach lining causing pain and discomfort.
- Food Poisoning: Illness resulting from consuming contaminated food.
- Pinworm Infestation (Springmask): Infection by small parasites causing anal itching.
- Winter Vomiting: Stomach flu leading to vomiting and gastrointestinal discomfort.
The Impact of Diet and Intestinal Flora: Recent research has highlighted the significance of the intestinal flora in health conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome, depression, and type 2 diabetes. The composition of the intestinal flora can be influenced by dietary choices, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet for gastrointestinal well-being.
Conclusion: A harmonious gastrointestinal system is essential for overall health. Understanding the functions of various organs, recognizing common disorders, and acknowledging the role of the intestinal flora can empower individuals to take proactive steps toward maintaining a healthy stomach and intestines. If faced with persistent discomfort or disruptive symptoms, seeking medical evaluation and guidance is paramount for effective management and improved quality of life.